Bullwhip Effect In Supply Chain: Definition, Example & Solutions
The bullwhip effect is a phenomenon in supply chain management that causes excessive inventory investment and overstocking at the supplier, importers, and wholesaler levels. It illustrates how a small, localized spike can have a much-greater-then-expected impact on an entire supply chain or production system.
This bullwhip occurs when a supply chain is not synchronized. With synchronization, we mean that supply chain partners collaborate and share data on sales exceptions, current inventory levels, etc.
This article has the following topics:
- What Is the Bullwhip Effect in Supply Chain Management?
- Example of the Bullwhip Effect in Action
- Causes of the Bullwhip Effect
- Impact on supply chain management
- Is MRP to blame?
- How can the supply chain reduce the bullwhip effect?
- Incorrect Demand Forecasts
- Bullwhip Effect In Supply Chain
- Increase Transparency Between Suppliers and Customers
- Limit Your Promotions and Sales
- Reduce Lead Times
- Where does the bullwhip effect have its greatest impact?
- Demand Driven MRP
- Within a company
The name bullwhip effect is derived from the cracking of a whip. When someone does swing a bullwhip, the end claps faster than the speed of sound, which causes the audible clap. Within a supply chain where a bullwhip effect is happening, energy is building up, and every supplier believes they need more inventory to ensure they can meet rising customer demand. When this upwards momentum claps, companies react by shrinking their inventory levels, which causes shortages again in a later phase. Because of this rise and fall, the bullwhip effect will become more prominent over time.
The best way to illustrate a bullwhip effect in supply chain management is with the following video:
What Is the Bullwhip Effect in Supply Chain Management?
The term "bullwhip effect" has been around in supply chain management circles for years and refers to decreasing lead time and increasing inventory and demand forecasts as forecasts and goods move in and out in increasingly larger, more complex global supply chains. It's a significant reason why inventory and demand forecasts are increasing faster today than just five years ago.
Example of the Bullwhip Effect in Action
A bullwhip effect's actual consequences can lead to many problems. Many companies use limited resources to produce the goods they believe they need. When the bullwhip effect occurs, many of these resources are wasted on excess inventory when companies could be using the capacity to meet customer demand.
Many companies that faced small shortages during covid-19 and the times after chose to buy in bulk. Buying in large quantities resulted in other companies being unable to purchase their needed parts. More than two years after the pandemic, many supply chains are still dealing with the fluctuations in demand. And while the covid was a major shift for any supply chain, the fluctuations in customer demand were not so great.
One supply chain example is WC paper. In many European countries, consumers began hoarding products such as toilet paper. These consumers then used that toilet paper and did not rebuy it until it ran out. Where the initial demand spike was significant, the long-term average demand did not change.
It is important to account for shifts in demand patterns in supply chain strategy. The supply chain is ultimately about serving customer demand.
Causes of the Bullwhip Effect
The term bullwhip effect comes from supply chain management consultant Dr. Jochen Kallen. Kallen observed the outcome in a supply chain in which he kept that, when purchasing one end, customers were highly reactive to the end being purchased, as if the end being bought was of lower quality and more likely to be out of stock. Kallen then compared this reaction to purchasing an entirely separate supply chain, in which purchasing one end was not an issue, and purchasing the entire end resulted in a much more significant reactive reaction.
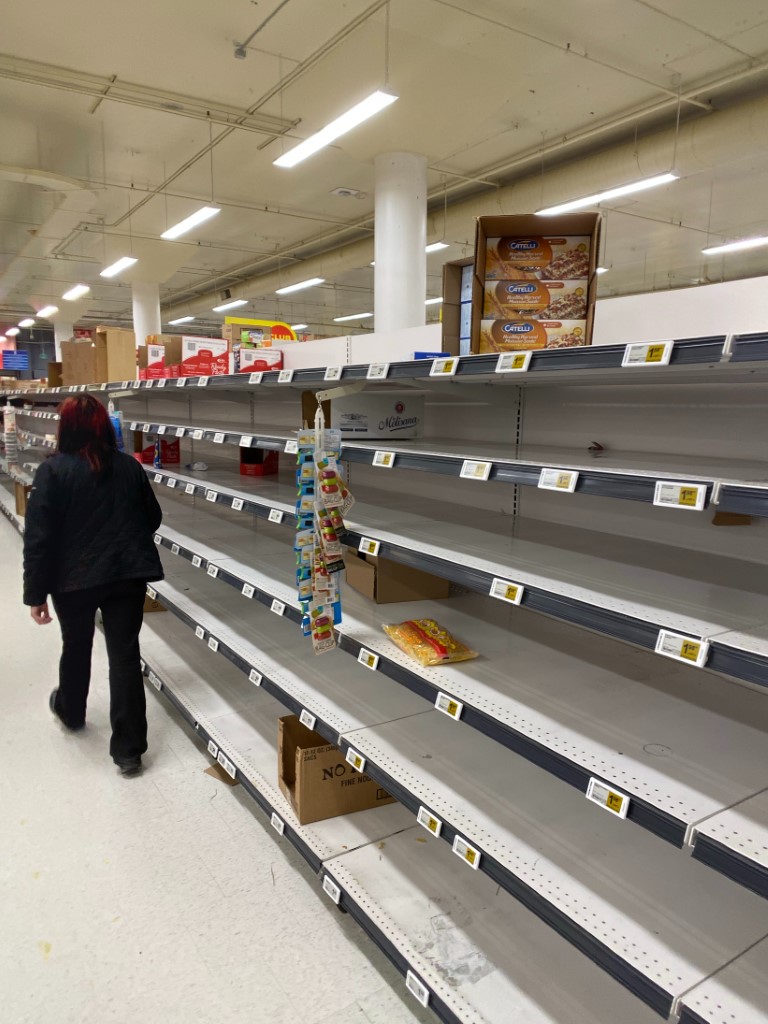

Impact on supply chain management
The bullwhip effect has been the most severe impact on supply chain management, as the parties involved in the manufacture or sales of a product, including wholesalers and retailers, are highly exposed to the potential effects of the sales or manufacturer.
Is MRP to blame?
When we analyze supply chain performance, we usually see that the cause of the bullwhip effect is enlarged by the mechanics of MRP or other forecasting methods. A slight movement on the demand side is changing production schedules across the supply chain. Because of this, the Bullwhip effect will naturally occur in MRP-guided systems. The result is excess inventory while also dealing with insufficient inventory to meet demand.
How can the supply chain reduce the bullwhip effect?
The best way to reduce the effects of the bullwhip effect is to reduce inventory levels and have stable prices, which will attract customers who may not otherwise be able to see, hear, or taste products they may like and may not even want. However, inventory reduction is a slow and challenging process to pull off successfully. Some techniques can help prevent the bullwhip effect from occurring. A system like Demand Driven MRP uses actual demand signals and minor capacity buffers to aid the supply chain and to be more agile when the market demand something extra.
Incorrect Demand Forecasts
The most common cause of demand forecast error is incorrect demand parameters. Demand planners often don't know they are experiencing an upswing in demand caused by the bullwhip effect. Did the demand change due to price fluctuations or seasonal demand? Did your competitor have production issues that caused the extra demand? These are all major factors contributing to distorted demand signals. Does your company have the required demand information to achieve high forecast accuracy? During the Certified Professional Planner course, we go into depth about these different parameters to recognize the bullwhip effect and know how to deal with it.
Increase Transparency Between Suppliers and Customers
It is a given that you won't buy from the supplier anymore when you can't see what you want to see. However, it is a far cry from saying that suppliers can't be transparent and make it a much easier and more enjoyable experience. This is especially important as supply chain management becomes increasingly crucial in increasingly globalized business.
Limit Your Promotions and Sales
To prevent the bullwhip effect from happening, it is an option to stop giving bulk discounts, and let customer demand only be what customers actually need. lower the minimum order quantity, use electronic data interchange, and work with your customers and suppliers to establish regular buying patterns. Price variations are also a contributing factor to the supply chain bullwhip effect
Reduce Lead Times
Lead time can be reduced with the help of supply. Reducing lead times can be done using inventory reduction, a technique where you reduce the number of products and materials on your production line and consolidate them into larger, cheaper quantities. This method can significantly improve inventory control and lead time.
Bullwhip Effect In Supply Chain
While the effects of the bullwhip effect on a supply chain may not immediately make sense, consider that, in most businesses, inventory control and inventory management have become a top concern for managers due to increased consumer expectations of a quicker and less expensive supply chain and order processes. Customer needs are also changing, forcing companies to carry enough stock and keep larger quantities to offer same-day shipping.


Where does the bullwhip effect have its greatest impact?
The effects of the bullwhip effect on supply have been greatest at times of market stress, as illustrated above. The effect has had the greatest impact on food production, as the increased demand from overstocking food products has been met with an overabundance from overstocking. Some raw material suppliers have chosen to move against the historical trends to meet demand when other companies are low on goods. These companies use the bullwhip effect to their advantage and prevent poor customer service by modeling managerial behavior.
Within a company
The effect can be caused by a change in inventory or demand for the product as well as a change in a supplier or an importer's inventory and demand, which may be driven by the changing needs of customers, the need to meet sales or other sales or other production and production-related demand, or the need to protect themselves from demand or inventory fluctuations.
Demand Driven MRP
One of the future trends to prevent the Bullwhip effect is DDMRP. This system will help by utilizing safety stock and using those to protect the company from demand changes and forecast errors. One of the pillars of DDMRP is to increase flow in a company resulting in becoming more agile. They do this by only starting a manufacturing run when there is real customer demand for a certain product. During the past few years, companies using DDMRP have proven to be more resilient and raise customer service during troubled times.